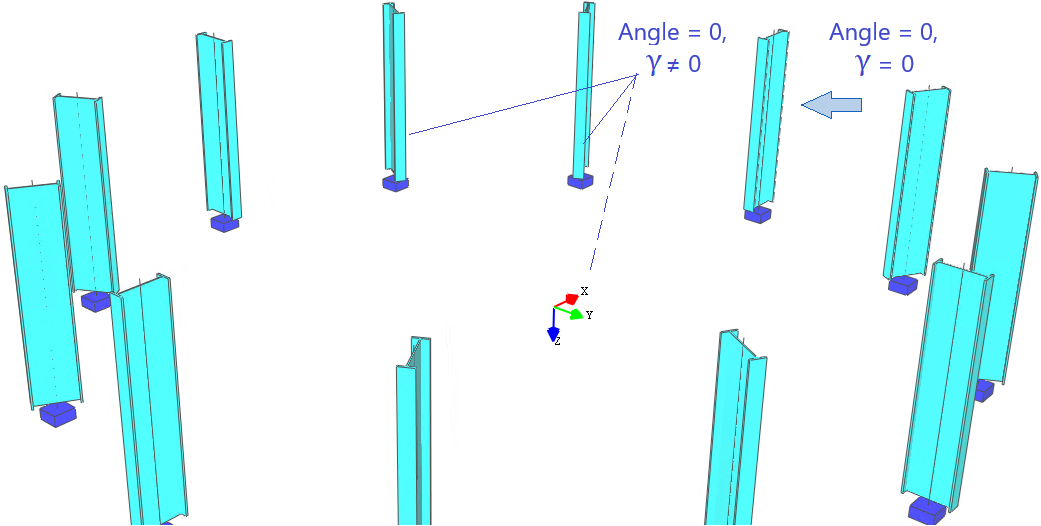
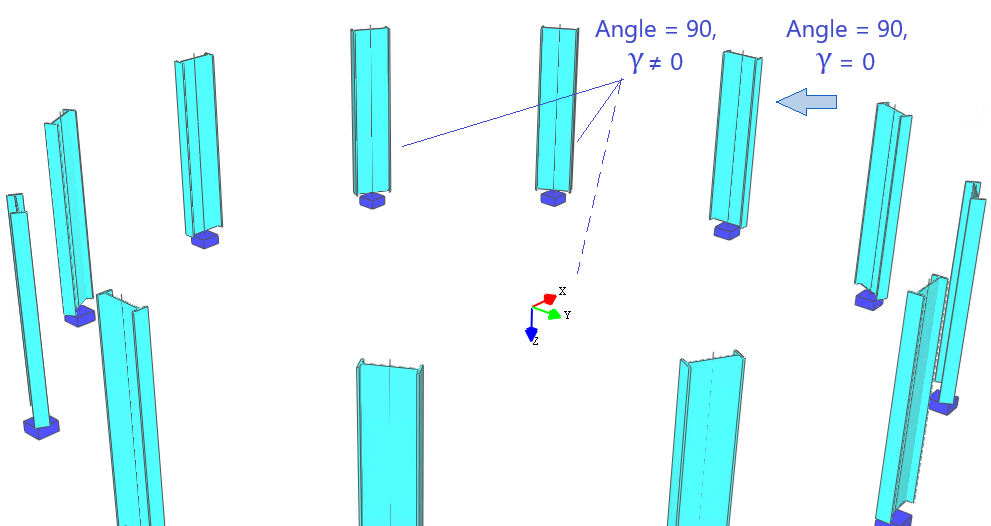
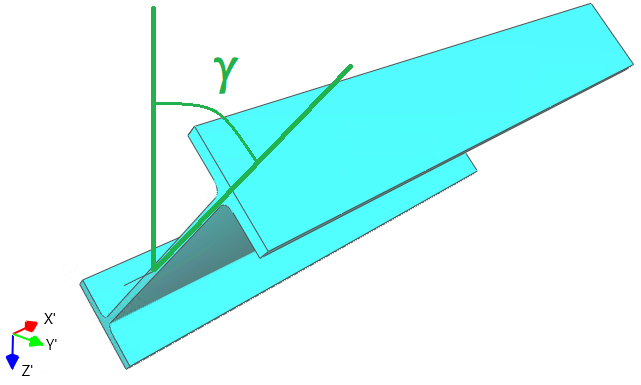
The counterclockwise rotation of a member around its local X' axis is defined by specifying the member rotation angle γ [°] in the "Member" table.
Notes:
1. The member rotation angle γ is available only in the 3D-Frame, 1.5D, and 2.5D packages;
2. This rotation angle does not affect the geometric characteristics of the member, but it does influence the overall stiffness of the computational system;
3. When the element is rotated by angle γ, all properties related to the local axes of the member, such as the cross-section and local loads acting on the element, are rotated as well;
4. When interpreting the analysis results, consider the member’s local coordinate system, rotated by angle γ, as the results are presented relative to this rotated system.
The initial rotation angle of the cross-section of the member, assuming γ is equal to 0 (γ = 0), can be defined in the "Section definition" part. The initial rotation angle of the cross-section is presented in the local axis system of the cross-section, and the geometric characteristics of the cross-section depend on this angle. This angle is universally applied across all packages (1D, 2D, 3D, etc.) as follows:

Interaction of cross-section rotation angle and member rotation angle γ can be treated as: