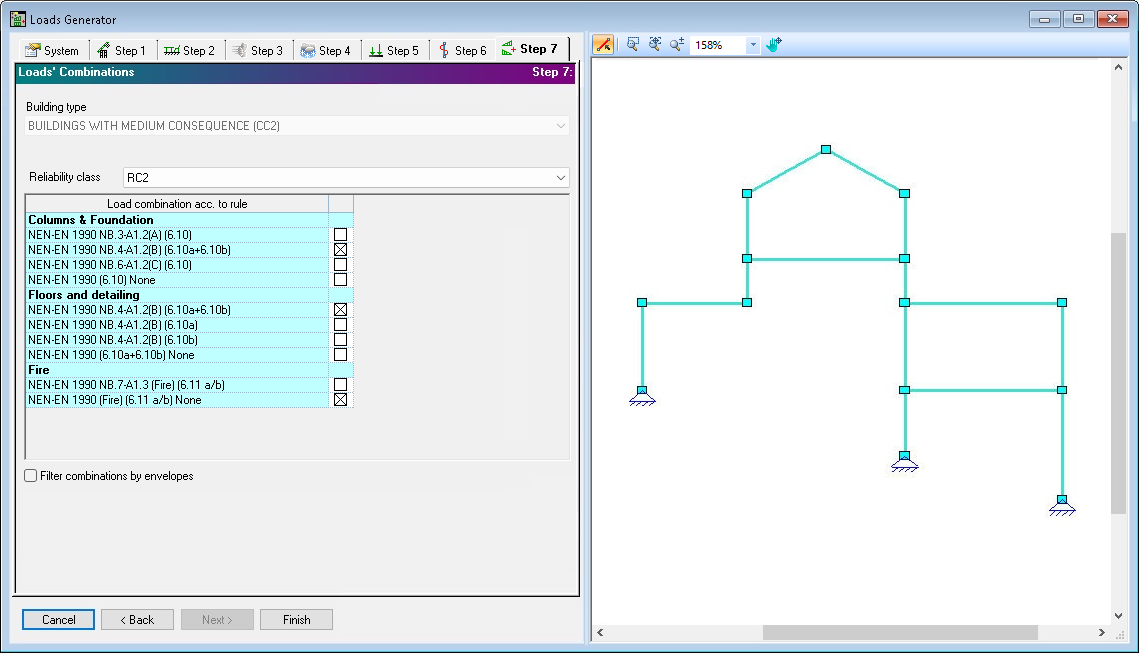
Fig 1. Loads Generator Step 7: Loads Calculations
Loads Generator creates loads combinations for the structure. Building type is defined by System and is dominating as informative factor.
Reference time [Years] is maximum building life-cycle time.
The reliability class index can be converted into annual failures of probability as follows:
|
Reliability Class |
Annual failure probability |
|
RC3 |
10E-7 |
|
RC2 |
10E-6 |
|
RC1 |
10E-5 |
Loads combinations are generated according to national code NEN-EN 1990 rules as shown on the grid. The rules may be ignored by checking the rule with index None.
Calculation of wind peak velocity pressure qp (NEN-EN 1991-1-4#4.5(4.8)) by using of mean wind velocity pressure vm²(z) (NEN-EN 1991-1-4#4.3.1(4.3)) contains probability factor cprob in the second degree as cprob².
In the standard NEN-EN 1991-1-4 the related articles for cprob wind are Art. 4.2, Note 4 & Art. 4.5:
|
4.2 Basic values NOTE 4 The 10 minutes mean wind velocity having the probability p for an annual exceedence is determined by multiplying the basic wind velocity vb in 4.2 (2)P by the probability factor, cprob given by Expression (4.2). See also EN1991-1-6.
4.5 Peak velocity pressure (1) The peak velocity pressure qp(z) at height z, which includes mean and short-term velocity fluctuations, should be determined.
qp(z) = (1 + 7 · Iv(z)) · ½ · ρ · vm²(z) = ce(z) · qb (4.8) qb = ½ · ρ · vb² (4.10)
In fact, this means, that qb(50 year) = ½ · ρ · vb² (Art. 4.5), where in case ref<>50 year the vb should be multiplied with cprob according to Art. 4.2, Note 4. This means, that: qb(x year) = ½ · ρ · (vb · cprob)² = (½ · ρ · vb²) · cprob² = qb(50 year) · cprob²
With: qp(z) = ce(z) · qb qp(x year) = ce(z) · qb(x year) = ce(z) · ½ · ρ · (vb · cprob)² = ce(z) · qb(50 year) · cprob² = qp(50 year) · cprob² |