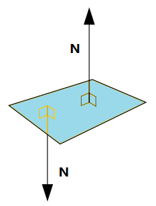
Definition of the p-load direction: normal vector of a plane "N", is described as:
1. The rule for the plane located local Z’ axis direction:
- Common case:
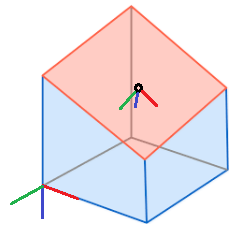
The local Z’ axis of the plane is parallel to the normal vector of the plane. The Z’ axis is directed to the lower half of space divided by plane (global direction of the Z axis).
- Exceptions:
a) In case of the normal of the plane is perpendicular to global Z axis, the local Z’ axis of the plane is parallel to the normal vector of the plane: the local Z’ axis of the plane is directed to the far half of space divided by plane (negative global Y direction);
b) In case of the normal of the plane is parallel to global X axis, the Z’ axis is directed to the right half of space divided by plane (positive global X direction).
2. The rule for the plane located local X’ axis:
a) If normal of a plane is parallel to global X axis, local X’ axis of the plane is directed to the near half of space divided by plane (positive global Y direction);
b) Otherwise, direction of the local X’ axis of the plane, always matches projection of global X axis into plane.
3. The rule for the plane located local Y’ axis:
The direction of the Y’ axis is a cross product of local Z’ and X’ directions of the plane.
Explanation pictures:
|
Case 1. Common case |
Case 2. Exceptional case. The normal to the plane is perpendicular to the global Z axis |
Case 3. Exceptional case. The normal to the plane is parallel to the global X axis |
|
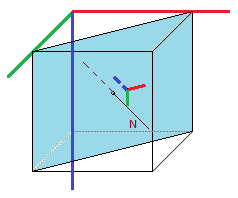
N ⊥ Z -> Z’ ∥ N |
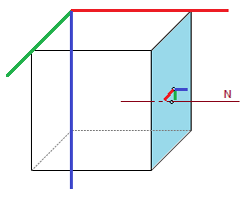
N ∥ X -> Z’ ∥ N and Z’ ∥ X |