The data of the calculations of the shear force reinforcement and the check results are shown in the tab V-shear:
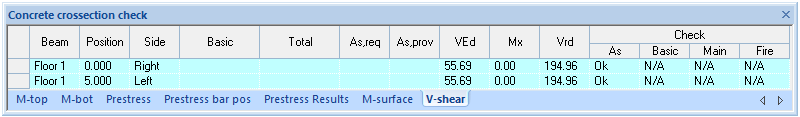
The same applies to the data in the longitudinal reinforcement. Available and calculated values of the required reinforcement are shown in the columns As,req and As,prov. Check results are shown in the tool tips, Reports and Structure View and change immediately after the input of the reinforcement.
Shear bearing capacity calculations:
A calculation of the shear resistance of the cross section is performed for two cases according to the EN 1992-1-1:2004 article 6.2 (the same assumptions can be applied for the NEN-EN 1992-1-1+C2:2011/NB:2011).
First case members without shear reinforcement:
Design shear resistance VRd,c is calculated according to the equation (6.2.a) and if this resistance is smaller than the shear force VEd the shear reinforcement is necessary. In calculations a longitudinal reinforcement and an axial force (if it exists) are taken into account. The calculated value is shown on the shear force diagram and it will also be presented in reports.
Second case members with shear reinforcement:
The design shear resistance VRd is calculated according to the equations (6.8) and (6.9). The equation (6.8) represents a member shear resistance depending on the quantity of the provided shear reinforcement. It is assumed that the shear reinforcement is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the member. The calculated capacity depends on the inner lever arm "z". The meaning of this lever arm is explained in Fig. 6.5 of the code.
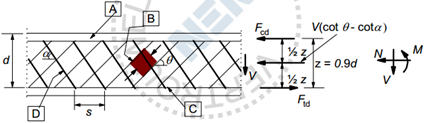
According to the code it is allowed to use the approximate "z" value equal to 0.9d. In our software it is calculated in a more sophisticated way. The lever arm between the design reinforcement tensile force and the design concrete compression force is calculated taking into account the real equilibrium in the cross section. So the value "z" strongly depends on the quantity of the provided longitudinal reinforcement and the reinforcement of the covering value. If the longitudinal reinforcement is still not provided for the "z" value calculations, a quantity of the required reinforcement will be used. The equation (6.9) establishes a limit capacity value of a compressed concrete strut.