Yagn-Boujinsky strength theory makes possible to take into account not only the difference in the material’s tensile and compression resistance, but also the shear resistance.
For Jagn-Boujinsky criterion, analysis is performed according to the following formula:
σJagn = 3 * (1 - X) * σA + L * [σA**2 * (F * P - 3) * σ1 * σ2]
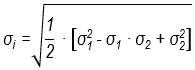
σA = 1/2 ⋅ (σ1 + σ2)
X = σu,t / σe,c
L = 1 / σe,c
F = σu,t / σu,s
P = σe,c / σu,s
Where:
σJagn – Jagn-Boujinsky stress criterion;
σi – intensity of stress;
σA – average stress (hydrostatic pressure);
σ1, σ2 – principal stresses, σ1 ≥ σ2;
σe,c – ultimate compression;
σu,t – ultimate tension;
σu,s – ultimate pure shear.