In case the Partial instability mode is used, boundary conditions as rotational stiffness Cr1 and Cr2 should be defined, to take into account the relation of the member and its environment, like connecting members and supports.
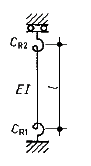
There are 2 ways to define this rotational stiffness:
- Geometrical stiffness analysis of the connecting members (EI, Length, member-end springs) and support springs:
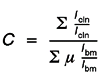
- Force stiffness analysis by the ratio of bending moment and rotation: Cr=M/φ:
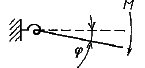
As the 1st one (Geometrical) is limited in functional way, in MatrixFrame® the 2nd method (Force) is implemented. In case of the Force stiffness analysis, a L.E. analysis should be performed with specific loads in a way that the resulting deformations are affine with the buckling curvature, to get the proper values for M and φ.