KTZ stiffness calculation
KTZ stiffness [Pa/m or N/m3] calculation is based on the assumptions and the algorithm taken from the German geotechnical literature:
KTZ stiffness is determined from soil layer(s) properties (depth of the soil layer and soil layer oedometric modulus). The algorithm describing the KTZ determination will be explained in-depth.
This method applies only on rectangular shaped supports; because of this an equivalent rectangle should be used for complex shapes describing planar supports. Knowing the rectangle dimensions (a, b), the next step is to determine a foundation parameter f. This parameter is determined from Table 1 considering two ratios:
- a/b
- z/b
where a = foundation length; b = foundation width; z = soil layer depth.
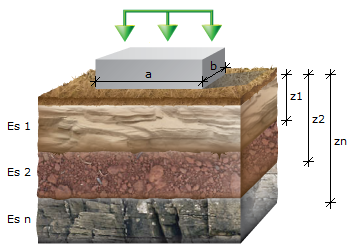
Fig 1. Soil stratification
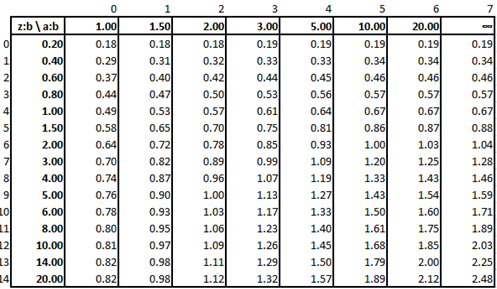
Table 1. Foundation parameter f
For a multi-layer soil, each layer will have its corresponding f (f1, f2, f3 ...) and its contribution to the final KTZ value:
- Layer 1:
- Layer 2:
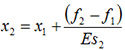
- Layer 3:
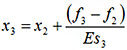
where Es represents the oedometric modulus.
The stiffness, KTZ is then calculated as follows:
- One-layer soil:
- Multi-layer soil:
For the beam structural element, where cross section width(b) is known, KTZ could be re-calculated to the distributed elastic stiffness Cz:
Cz [kN/m3⋅m] = KTZ ⋅ b.